A ball mill is a type of grinder used to grind and blend bulk material using different sized balls. Ball mills are commonly used for crushing and grinding the materials into an extremely fine form.
The ball mill contains a hollow cylindrical shell that rotates about its axis. This cylinder is filled with balls that are made of stainless steel or rubber to the material contained in it. Ball mills are classified as attritor, horizontal, planetary, high energy or shaker.
The ball mill is a tumbling mill that uses steel balls as the grinding media. The length of the cylindrical shell is usually 1–1.5 times the shell diameter
Ball mills are filled up to 40% with steel balls (with 30–80 mm diameter), which effectively grind the ore. The material that is to be ground fills the voids between the balls. The tumbling balls capture the particles in ball/ball or ball/liner events and load them to the point of fracture.

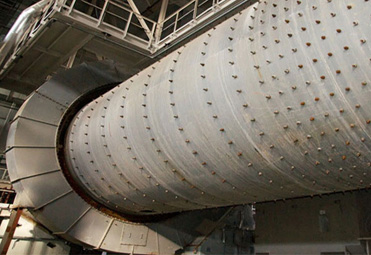

A ball mill consists of a hollow cylindrical chamber which rotates about a horizontal axis, and the chamber is partially filled with small balls made of steel, tungsten carbide, zirconia, agate, alumina, or silicon nitride having diameter generally 10 mm. The inner surface area of the chamber is lined with an abrasion-resistant material like manganese, steel, or rubber. The magnet, placed outside the chamber, provides the pulling force to the grinding material, and by changing the magnetic force, the milling energy can be varied as desired. The ball milling process is carried out for approximately 100–150 h to obtain uniform-sized fine powder. In high-energy ball milling, vacuum or a specific gaseous atmosphere is maintained inside the chamber. High-energy mills are classified into attrition ball mills, planetary ball mills, vibrating ball mills, and low-energy tumbling mills.
It is an inexpensive and easy process which enables industrial scale productivity. As grinding is done in a closed chamber, dust, or contamination from the surroundings is avoided.
It is possible to mill the powder in the dry or wet state to produce different results. Wet milling produces smaller particles, but dry milling has the advantage that the liquid milling media does not need to be removed at the end of the process. This not only saves time but also prevents the formation of hard agglomerates which can result when liquids are removed from powder suspensions.
